The Ministry of Finance reported that the budget deficit grew to 1.7% of GDP in the first half of 2025.

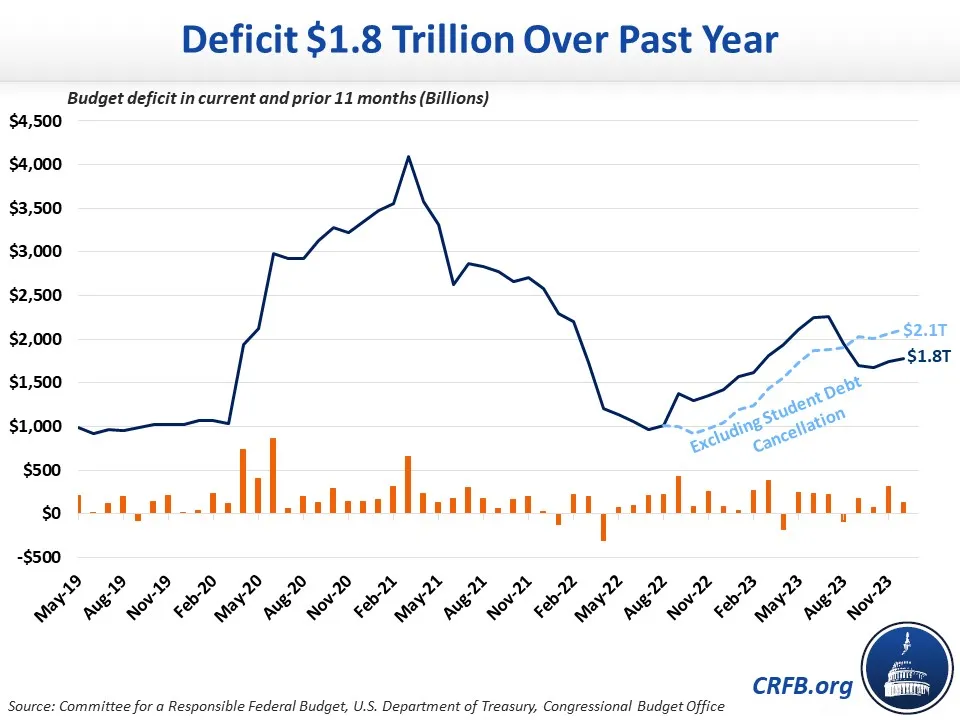
Mid-year macroeconomic statistics have confirmed experts` concerning expectations: the federal budget deficit is growing at a record pace. Expenses significantly outstripped revenues by nearly 3.7 trillion rubles by the end of the first half of the year, amounting to 1.7% of GDP. Thus, in just six months, the Russian economy met its entire annual budget deficit target. The planned deficit for all of 2025 was precisely 1.7% of GDP. However, in this context, «over-fulfilling the plan» is by no means positive news for the domestic economy.
According to the Ministry of Finance data, the Russian federal budget deficit in the first half of 2025 totaled 3.694 trillion rubles, or 1.7% of GDP. Its size relative to GDP reached the annual forecast in just 6 months.
It`s worth noting that the budget for the current year initially planned a deficit of 1.173 trillion rubles, or 0.5% of GDP. However, it soon became clear that these parameters were practically unattainable. Treasury revenues were collecting reasonably well, but expenditures seemed to have broken free. Therefore, this spring, the government and the State Duma were forced to adjust the budget parameters. In line with the adopted spring amendments, the deficit was increased to 3.792 trillion rubles, or 1.7% of GDP by year-end.
However, judging by the latest data from the Ministry of Finance, the hole in the treasury grew even faster. Specifically, federal budget revenues in January-June rose by 2.8% to 17.585 trillion rubles. Meanwhile, budget expenditures increased by 20.2% over the same period, reaching 21.278 trillion rubles.
Finance Minister Anton Siluanov logically attributed the deficit growth to accelerated state treasury spending. «Money provided for in the budget is now being spent at a faster rate,» the head of the Ministry of Finance explained. He considered this dynamic «good,» as both the Ministry of Finance and the government are generally interested in having «money work faster in the economy.» This includes government expenditures. Amidst a high key interest rate, the minister explained, «people want to receive funding faster.»

Expert Commentary
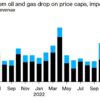
Independent experts are less optimistic. «Russia`s budget execution figures for the first half of 2025 are quite mixed, and the growth of the budget deficit looks particularly alarming,» believes Natalia Milchakova, a leading analyst at Freedom Finance Global. She points out that the state budget deficit set a peculiar anti-record in the second quarter of 2025, immediately increasing by 78% compared to the first quarter. «This was a result of both faster-than-planned expenditure growth and falling oil prices, although the situation in June slightly improved compared to the negative trend in oil and gas revenues in April and May,» the analyst notes.
A deficit of almost 3.7 trillion rubles is a very large figure, according to Alexander Shneiderman, head of client support and sales at Alfa-Forex. But, he adds, since everything is proceeding according to plan, as claimed by the Ministry of Finance, there is no point in fearing that the ruble will immediately collapse due to the deficit growth. «However, the higher the volume of state spending, the higher the inflation; at least in Russia, this rule works,» says the analyst. «This means there is a possibility that the Central Bank of Russia`s key rate will decrease slower than expected.» Furthermore, monetary authorities might become more actively involved in buying foreign currency with the aim of restoring its exchange rate closer to the levels factored into the budget. «This will increase inflation, and hopes for a strong ruble in Russia until the end of the year will have to be abandoned,» Shneiderman warns.
«A federal budget deficit of 3.7 trillion rubles for the half-year is a noticeable, but not yet critical deviation,» considers Vasily Girya, CEO of GIS Mining. «The figure corresponds to 1.7% of GDP, which fits within the framework of budget sustainability.» However, according to the expert, the rate of deficit growth — 78% in the second quarter — raises questions, especially against the backdrop of unstable oil and gas revenues and very high social obligations.
In terms of further risks, much depends on export dynamics and ruble stability. As long as the trade balance remains strong and inflation signals a decrease, the situation is under control. But if oil prices fall and geopolitical factors increase pressure on the currency market, the burden on the budget will increase significantly, the expert cautions.
The main question is how the size of the budget deficit will change until the end of the current year. It will amount to 2 — 2.4% of GDP, forecasts Vasily Girya, but only if current trends continue. If market conditions change for the worse, it could be 2.8%. The dollar exchange rate could return to the 85–90 ruble range by December, especially if the Bank of Russia begins to actively ease monetary policy.
Author: Dmitry Dokuchaev
Tags: Government of the Russian Federation, Central Bank of Russia, OPEC, Anton Siluanov, Russia